Understanding the basics of Architectural 3D BIM Modeling Services.
Hello and welcome back to our new blog. We are Silicon Valley, a firm where we create CAD drawings and models for structures. Today we will share our knowledge of the basics of Architectural 3D BIM Modeling and related services about how it works and benefits in real-life buildings.
The design and building process can now be done more accurately and efficiently for professionals like architects and engineers thanks to the widespread use of architectural 3D BIM modeling. We will examine the fundamentals of architectural 3D BIM modeling services in this post, including their nature, operation, and advantages.
What are Architectural 3D BIM Modeling?
Architectural 3D Modeling Services is the process of creating a three-dimensional detailed digital replica of a building in the world of a computer. Beyond superficial aesthetics, this complex computer model goes deeply into the structural makeup and operational systems of the imagined building.
For architects, builders, and a variety of everyone involved, the digital version acts as a dynamic compass, expediting the design and building processes with unmatched efficiency. In particular, it has the extraordinary capacity to autonomously recalibrate the model in response to changes, providing a degree of adaptability that is essential in the constantly changing world of architecture.
It serves as a harmonizing medium that allows many professionals to combine their experience, facilitating smooth communication and ultimately producing a cogent and well-coordinated result. Additionally, it serves as a watchful sentinel against mistakes, defending the project's integrity by averting mistakes that could be expensive and time-consuming.
However, the benefits of architectural 3D BIM modeling go beyond their capacity for organization. It acts as a visionary tool, giving a sneak peek of the building's ultimate aesthetic and verifying that it adheres to the original concept. Additionally, it has the capacity to assess the strength of the structure and its operational effectiveness, guaranteeing that it is more than simply a work of art but also a secure, useful, and resource-saving marvel.
Architectural 3D BIM modeling serves as a vital engine for planning, guiding, and managing the full lifecycle of a project, from its infancy to its physical realization.
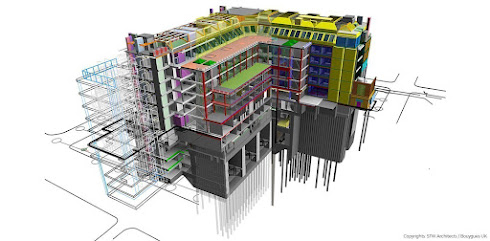
Architectural 3D Building Information Modelling (BIM) is a digital graphic representation of a building's structural and operational features. It entails building a 3D model of the structure that not only displays its geometry but also contains details on the parts, materials, and connections between them.
The basic principles of 3D BIM modeling for architecture are as follows:
Software Tools:
BIM modeling is often carried out with the aid of specialized programs like Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, or Vectorworks. These programs are intended for building, editing, and managing BIM models.
Building components :
Buildings are represented in architectural 3D BIM modeling as a group of building elements, such as walls, floors, roofs, doors, windows, and other architectural elements.
3D model:
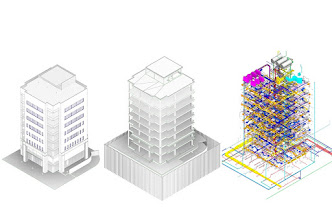
The shape and geometry of these architectural components are defined to produce the 3D model. In three-dimensional space, this comprises their size, shape, and location.
Modelling Parametrically:
Parametric modeling is possible with BIM software, meaning that modifications to one element update all associated elements automatically. For instance, if you modify a wall's height, the software will also change the ceiling's position and the positions of any other related objects.
Connectivity of data:
BIM incorporates non-graphical information to go beyond 3D modeling. Materials qualities, cost projections, energy efficiency statistics, and maintenance data are some examples of this data. BIM is useful for sustainability analysis, facility management, and project management as a result.
Levels of Detail (LOD):
BIM models come in a variety of levels of depth, from straightforward conceptual drawings to more detailed models that are ready for building. Depending on the stage of the project and the model's intended purpose, the LOD changes.
Collaboration:
Collaboration between engineers, builders, architects, and other partners is facilitated by BIM. Working across disciplines on the same model improves coordination and lowers errors.
Version Monitoring:
Version Monitoring and change tracking are two features that BIM software often provides, helping to keep track of model modifications and guaranteeing that everyone is using the most recent information.
Visualization:
BIM models can be used for 3D visualization, rendering, and virtual tours that aid in a better understanding of the design and construction process by clients and stakeholders.
Modelling and Examination:
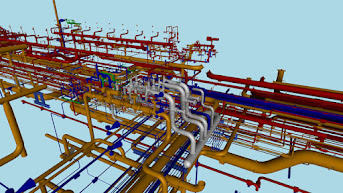
To find and resolve conflicts between various building systems, clash detection, energy performance modeling, and structural analysis are just a few of the analyses that may be performed using BIM.
Documentation creation:
BIM software can generate architectural plans, schedules, and reports automatically, saving time and lowering the possibility of documentation errors.
Data Exchange:
Data sharing with other tools and stakeholders in the building and operations process is made possible by the ability of BIM models to be exported to or connected to a variety of file formats.
Economic and Legal Considerations:
BIM might have economic and legal consequences. The use of BIM, intellectual property rights, and obligations connected to the BIM model should all be covered in conventions and agreements.
Modern builders and architect practices require the use of architectural 3D BIM modeling, which provides improved efficiency, teamwork, and data-rich project management throughout the full lifecycle of the building, from its conception and building to operation and maintenance.
Architectural 3D BIM Modeling provides a wide array of services, including:
- Creating realistic 3D visualisations of designs using visualisation and rendering.
- Finding and fixing design faults early on through virtual prototyping.
- Detecting conflicts between structural elements is known as clash detection.
- estimating the expenses of a project and the amount of materials needed.
- Safety standards compliance is ensured through structural analysis.
- scheduling and resource management optimisation in development.
- Collaboration: Facilitating communication between interested parties.
- Data integration for facility management activities following construction.
- Enhancing sustainability and energy efficiency through energy analysis.
- Maintaining openness and legal compliance through documentation.
Comments
Post a Comment