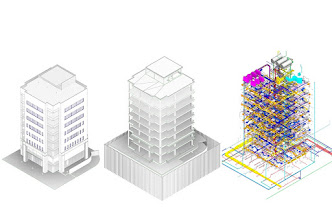
What is Pre Engineered Building Design?
Silicon Valley is a hub for innovation and technology, and this is reflected in the pre-engineered building design and drafting CAD services that are available in the area. Companies in Silicon Valley are constantly looking for ways to save time and money, and pre-engineered buildings offer a great way to do this.
Pre-engineered buildings are made from prefabricated components that are assembled on-site. This allows for faster construction times and lower costs. Additionally, pre-engineered buildings can be customized to meet the specific needs of the building owner, which is important in a region like Silicon Valley where there is a wide variety of businesses with different requirements.
Introduction Of Pre Engineered Building Design
Pre Engineered Building Design (PEB) is a method of constructing buildings using pre-fabricated structural components that are designed and manufactured off-site. These components, including columns, beams, roof trusses, and wall panels, are engineered to fit together seamlessly, allowing for efficient and rapid assembly on the construction site. PEB systems are known for their cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and shorter construction timelines compared to traditional building methods.
Pre-engineered building (PEB) design is a type of building construction that uses prefabricated components to create a structure. The components are designed and engineered in advance and then manufactured in a factory. This allows for faster construction times and lower costs than traditional stick-built construction.
PEBs are typically made of steel, but can also be made of concrete or wood. The steel frame is the main structural element of the building, and it is supported by columns and beams. The walls and roof are made of metal panels, and the windows and doors are pre-hung.
PEBs can be used for a variety of applications, including warehouses, factories, retail stores, and schools. They are also a popular choice for agricultural buildings and sports facilities.
Pre-engineered building (PEB) design offers several advantages over traditional stick-built construction, including:
- Faster construction times: PEBs can be constructed much faster than traditional stick-built buildings. This is because the components are prefabricated and can be assembled on-site in a matter of weeks. This can be a major advantage if you need to get your building up and running quickly.
- Lower costs: PEBs are typically more cost effective than traditional stick-built buildings. This is because they require less labor and materials to construct. This can save you a significant amount of money on your building project.
- Greater flexibility: PEBs can be customized to meet specific needs. This makes them a good choice for buildings with complex layouts or unusual requirements. You can choose from a variety of wall panels, roof styles, and other features to create a building that meets your exact specifications.
- Durability: PEBs are very durable and can withstand harsh weather conditions. They are also fire-resistant and can meet seismic codes. This means that your building will be able to withstand the elements and provide a safe and secure environment for years to come.
- Sustainability: PEBs are made from recycled materials and can be easily recycled at the end of their lifespan. This makes them a more sustainable option than traditional building materials.
Here are some additional benefits of pre-engineered building design:
- Reduced risk of errors: Because the components are prefabricated in a controlled environment, there is less risk of errors during construction. This can save you time and money in the long run.
- Improved quality control: The components of PEBs are manufactured to strict quality standards. This ensures that your building will be built to a high standard and will last for many years.
- Easier maintenance: PEBs are relatively easy to maintain. The components are accessible and can be easily repaired or replaced if necessary.
- Better energy efficiency: PEBs can be designed to be energy efficient. This can save you money on your energy bills.
If you are looking for a cost-effective, durable, and sustainable building solution, pre-engineered building design is a good option to consider.
What are the disadvantages of pre-engineered buildings?
Pre-engineered buildings (PEBs) offer some advantages over traditional stick-built construction, but they also have some disadvantages. Here are some of the potential drawbacks of PEBs to consider:
- Limited customization: PEBs are typically less customizable than stick-built buildings. This is because they are designed and engineered in advance, and the components are prefabricated to specific specifications. If you need a building with a very specific layout or design, PEBs may not be the best option.
- Higher initial costs: The upfront costs of PEBs can be higher than traditional stick-built buildings. This is because of the cost of prefabrication and transportation. However, the long-term costs of PEBs are often lower, due to their durability and energy efficiency.
- Less flexibility: PEBs are less flexible than stick-built buildings. This is because they are designed to be a specific size and shape. If you need a building that can be easily expanded or modified in the future, PEBs may not be the best option.
- Limited availability: PEBs are not as widely available as traditional stick-built buildings. This is because they require specialized manufacturing and construction methods. If you live in a rural area, you may have difficulty finding a PEB supplier.
- Potential for noise pollution: PEBs can be noisy, especially during construction. This is because the components are assembled on-site using heavy machinery. If you are concerned about noise pollution, you may want to consider a different type of building construction.
Overall, PEBs offer many advantages over traditional stick-built construction. However, they also have some potential drawbacks. It is important to weigh the pros and cons carefully before deciding whether or not a PEB is the right choice for your project.
What is an example of a pre-engineered building?
An example of a pre-engineered building is a warehouse. Pre-engineered building systems are commonly used to construct warehouses due to their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and quick construction timeline. In this context, a warehouse could be designed and built using pre-fabricated columns, beams, roof trusses, and wall panels that are manufactured off-site and then assembled on the construction site.
The standardized design of pre-engineered building systems allows for the creation of large, open interior spaces, which is ideal for warehouses that require ample storage and working areas without the obstruction of interior columns. The components are engineered to work together seamlessly, ensuring structural integrity and stability.
Furthermore, warehouses often have clear-span designs, where the interior space is free from columns or supports. This design feature maximizes usable space and provides flexibility for storing goods and equipment.
By using pre-engineered building systems, the construction of a warehouse can be completed in a shorter time compared to traditional construction methods. This time-saving factor is particularly valuable for businesses that need to establish operational spaces quickly.
Overall, warehouses are a prime example of how pre-engineered building design can offer a practical and efficient solution for constructing functional structures in various industries.
What is the difference between pre-engineered buildings and conventional buildings?
What is the lifespan of a pre-engineered metal building?
The lifespan of a pre-engineered metal building (PEB) can vary depending on several factors, including the quality of the materials used, the climate in which it is located, and the level of maintenance it receives.
However, most PEBs can last for 50 to 100 years with proper care.
PEBs are made from steel, which is a very durable material. Steel is resistant to corrosion and can withstand harsh weather conditions. PEBs are also fire-resistant and can meet seismic codes. This means that they are well-suited for use in a variety of climates and locations.
The lifespan of a PEB can be extended by regular maintenance. This includes inspecting the building for signs of damage, repairing any damage that is found, and painting the building to protect it from the elements. If a PEB is properly maintained, it can last for many years.
Here are some tips for extending the lifespan of your pre-engineered metal building:
- Inspect the building regularly: Inspect the building for signs of damage, such as rust, leaks, or cracks. Repair any damage that is found as soon as possible.
- Paint the building regularly: Painting the building will help to protect it from the elements and extend its lifespan.
- Keep the gutters and downspouts clean: Clogged gutters and downspouts can lead to water damage. Make sure to keep them clean and free of debris.
- Avoid overloading the building: Overloading the building can put stress on the structure and shorten its lifespan. Make sure to only store or use the building for its intended purpose.
- Have the building inspected by a professional every 5 to 10 years: A professional inspection can help to identify any potential problems with the building and recommend repairs or maintenance.
By following these tips, you can help to ensure that your pre-engineered metal building lasts for many years to come.
📣NOTE: Navigating the Challenges of BIM Coordination Services: Tips and Best Practices
Where are pre-engineered structures best used?
Pre-engineered structures are best used in applications where speed, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility are important factors. Here are some examples of where pre-engineered structures are commonly used:
- Warehouses: Warehouses are a classic example of a pre-engineered structure. They are typically large, open structures that need to be built quickly and cost-effectively. PEBs are ideal for warehouses because they can be customized to meet the specific needs of the business.
- Factories: Factories are another common type of pre-engineered structure. They need to be strong and durable to withstand the weight of heavy machinery and equipment. PEBs can be designed to meet the specific needs of the factory, including the size, shape, and layout.
- Retail stores: Retail stores are often built with pre-engineered structures because they can be customized to meet the specific needs of the store. For example, the building can be designed to have a large storefront or a specific number of parking spaces.
- Office buildings: Office buildings can also be built with pre-engineered structures. They are typically smaller than warehouses or factories, but they can still be customized to meet the specific needs of the business.
- Schools: Schools are a good example of a pre-engineered structure that needs to be both durable and flexible. PEBs can be designed to meet the specific needs of the school, including the number of classrooms, the size of the library, and the layout of the playground.
- Agricultural buildings: Pre-engineered structures are often used for agricultural purposes, such as barns, silos, and grain elevators. They are well-suited for these applications because they are durable, easy to maintain, and can be customized to meet the specific needs of the farmer.
- Sports facilities: Pre-engineered structures are also used for sports facilities, such as stadiums, arenas, and gymnasiums. They are ideal for these applications because they can be built quickly and cost-effectively, and they can be customized to meet the specific needs of the sport.
- Military applications: Pre-engineered structures are also used for military applications, such as barracks, hangars, and storage facilities. They are well-suited for these applications because they are durable, portable, and can be quickly assembled and disassembled.
Overall, pre-engineered structures are a versatile and cost-effective building option that can be used for a variety of applications. If you are looking for a building that can be built quickly, cost-effectively, and customized to meet your specific needs, a pre-engineered structure may be a good option for you.
What materials are used in pre-engineered buildings?
- Structural Steel: Forms framework (columns, beams, trusses).
- Metal Panels: Roofing and wall panels for weather protection.
- Concrete: For foundations, slabs, and walls (if used).
- Insulation: Maintains interior temperatures and energy efficiency.
- Doors/Windows: Roll-up doors, and windows for functionality.
- Cladding: Exterior finishes like metal, composite, and masonry.
- Fasteners: Bolts, and screws secure building components.
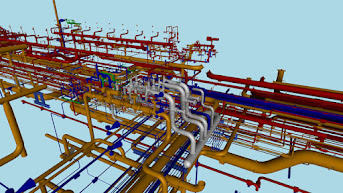
- Electrical/HVAC Systems: Wiring, lighting, HVAC for utilities.
- Fire Safety: Sprinklers, systems based on usage.
This mix ensures durability, practicality, and design versatility in pre-engineered buildings for various industries.
✅Read Our new blog on Structural Steel Detailing Services.
What are pre-engineered buildings mainly done with?
Pre-engineered buildings (PEBs) are mainly done with steel. Steel is a strong, durable, and fire-resistant material that is well-suited for use in buildings. It can be bent and shaped to create a variety of structures, and it can be easily transported and assembled.
Here are some of the reasons why steel is the most common material used in PEBs:
- Strength: Steel is one of the strongest building materials available. It can withstand heavy loads and harsh weather conditions.
- Durability: Steel is also very durable and can last for many years with proper maintenance.
- Fire resistance: Steel is fire-resistant and can meet fire codes. This is important for buildings in areas that are prone to wildfires or other fire hazards.
- Cost-effectiveness: Steel is a relatively inexpensive building material. This can save you money on the construction of your PEB.
- Versatility: Steel can be used to create a variety of building structures, from simple warehouses to complex office buildings. This makes it a good choice for a wide range of applications.
- Ease of transportation and assembly: Steel components are lightweight and easy to transport. This can save you money on the cost of shipping and construction. Steel components can also be easily assembled by a team of skilled workers.
What are the characteristics of a pre-engineered building?
Here are some of the characteristics of a pre-engineered building (PEB):
- Prefabricated components: PEBs are made from prefabricated components that are assembled on-site. This allows for faster construction times and lower costs.
- Steel frame: The main structural element of a PEB is a steel frame. Steel is strong, durable, and fire-resistant, making it a good choice for buildings in a variety of climates and locations.
- Metal panels: The exterior walls and roof of a PEB are typically made from metal panels. Metal panels are strong, durable, and weather-resistant.
- Windows and doors: PEBs typically have large windows and doors to let in natural light. Windows and doors can be customized to meet the specific needs of the building.
- Insulation: PEBs can be insulated to meet energy efficiency standards. Insulation can help to reduce heating and cooling costs.
- Finishes: The interior and exterior of a PEB can be finished to meet the specific needs of the building owner. Finishes can include paint, flooring, and roofing.
What construction type is a pre-engineered metal building?
Pre-engineered metal buildings (PEBs) are a type of structural steel building and Structural Design And Drafting. Structural steel is a strong, durable, and versatile material that is well-suited for use in buildings. It can be bent and shaped to create a variety of structures, and it can be easily transported and assembled.
PEBs are made from prefabricated components that are assembled on-site. This allows for faster construction times and lower costs. The components are designed and engineered in a factory, which ensures that they are consistent and meet quality standards. This also reduces the risk of errors during construction.
The main structural element of a PEB is a steel frame. The frame is made from I-beams and columns that are connected with bolts. The frame is then covered with metal panels, which provide the exterior walls and roof of the building. The metal panels are typically made from galvanized steel, which is weather-resistant and fire-resistant.
PEBs can be customized to meet the specific needs of the building owner. The size, shape, and layout of the building can be customized to meet the specific requirements of the project. The type of metal panels and the insulation can also be customized to meet the specific climate and energy efficiency requirements.
What is the difference between a pre-engineered metal building and a steel building?
Pre-engineered metal buildings (PEBs) and steel buildings are both types of structures that are made from steel. However, there are some key differences between the two types of buildings.
- Construction: PEBs are constructed using prefabricated components that are assembled on-site. This allows for faster construction times and lower costs. Steel buildings, on the other hand, are typically constructed using more traditional methods, which can take longer and be more expensive.
- Flexibility: PEBs are more flexible than steel buildings in terms of their design and layout. PEBs can be customized to meet the specific needs of the building owner, while steel buildings are typically more limited in their design options.
- Cost: PEBs are typically more cost-effective than steel buildings. This is because they require less labor and materials to construct. Steel buildings, on the other hand, can be more expensive due to the more traditional methods of construction.
- Durability: PEBs and steel buildings are both very durable and can withstand harsh weather conditions. However, PEBs may be more durable in certain situations, such as in areas with high winds or seismic activity.
- Energy efficiency: PEBs can be more energy-efficient than steel buildings. This is because PEBs can be designed to be more airtight, which can help to reduce heating and cooling costs. Steel buildings, on the other hand, may not be as airtight and can be more energy-intensive to operate.
Ultimately, the best type of building for you will depend on your specific needs and budget. If you are looking for a building that is fast to construct, cost-effective, and flexible, then a PEB may be a good option for you. If you are looking for a building that is very durable and energy-efficient, then a steel building may be a better choice.
Thank you all viewers for your precious time to read the blog. we are Silicon Valley Infomedia Pvt. Ltd. Leads in CAD Drawings and Drafting services worldwide.
check our more blogs from the Blogger profile for more information.



Comments
Post a Comment